Related Questions:
– Compare the different Sequence models (RNN, LSTM, GRU, and Transformers)
– What is Natural Language Processing (NLP) ? List some of the common NLP tasks
– What are Language Models? Discuss the evolution of Language Models over time
Sequence data
Sequence data refers to a type of data where the order of elements is significant, and the elements are typically arranged in a specific sequence or chronological order. In sequence data, each element in the sequence is related to the ones that come before and after it, and the way these elements are ordered provides context, meaning, and structure to the data.
Here are some key characteristics of sequence data:
- Order Matters: In sequence data, the arrangement of elements is important. Changing the order of elements can lead to different meanings or interpretations. For example, in natural language processing, the order of words in a sentence conveys the sentence’s meaning.
- Temporal or Sequential Relationship: Sequence data often exhibits a temporal or sequential relationship. This means that the elements are typically collected or observed in a specific order over time. Time series data such as stock price, for instance, records values at different time points.
- Variable Length: Sequences can have variable lengths. In natural language, sentences can be of different lengths, and in genomics, DNA sequences can vary in length depending on the organism.
Examples of sequence data
- Time Series Data: This is a common type of sequential data where measurements are taken at regular intervals over time. Examples include stock prices, temperature readings, and sensor data.
- Natural Language Text: Textual data, such as sentences or paragraphs, is inherently sequential. The order of words matters to convey meaning, context, and relationships between words.
- Speech Signals: Audio signals from spoken language are sequential. Phonemes, syllables, and words are organized sequentially to form sentences.
- Music: Musical notes in a composition are ordered sequentially to create melodies, harmonies, and rhythms.
- DNA Sequences: In genetics, DNA sequences represent the arrangement of nucleotides in a specific order, carrying genetic information.
- Video Frames: In video data, each frame is a snapshot of a scene at a specific time. The sequence of frames creates the illusion of motion.
- User Actions / Clickstream data: User interactions on a website or application, such as clicks or keystrokes, occur sequentially and can be used to understand user behavior.
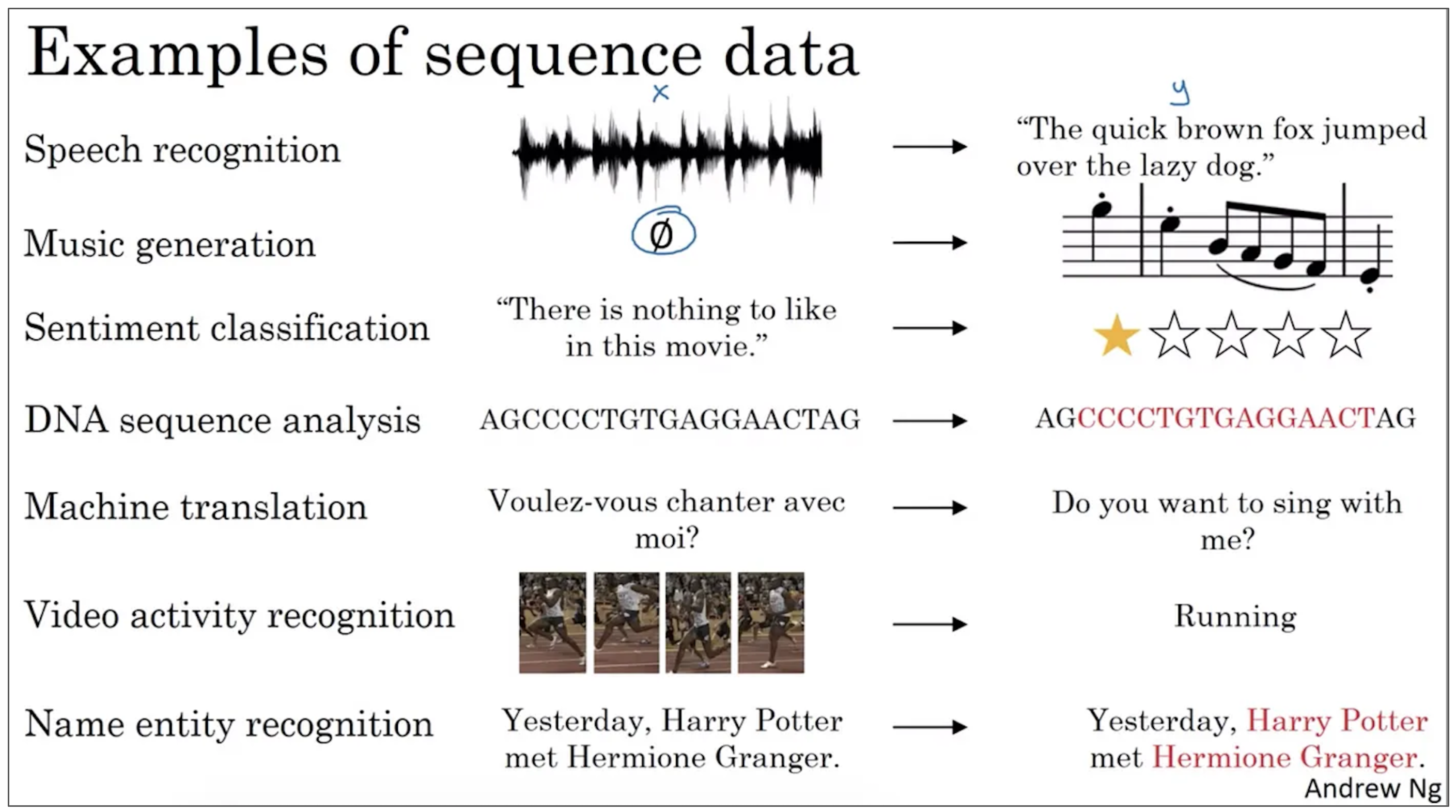
Source: Sequence Models course by DeepLearning.AI
Analyzing and modeling sequence data often requires specialized techniques and algorithms. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Transformers and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are commonly used in deep learning for handling sequence data, as they can capture dependencies and patterns over time. Additionally, traditional statistical methods like autoregressive models are also employed for time series analysis and forecasting.
Non-Sequential Data
This contrasts with non-sequential data, where the order of elements does not carry any particular significance. For example, Tabular data for classifying whether a payment application is fraud or not. Spreadsheet consist of rows and columns where each row represents an individual payment application and each column represents a feature (business type, location, identity score, tenure etc.). The order of rows generally doesn’t hold any temporal context.
Video Explanation
- In the “Sequence Model Complete Course” lecture video, Prof. Andrew Ng explains the concept of Sequence data and Sequence models using multiple examples (Runtime: First 12 mins). In the rest of the video, he goes deeper into each type of Sequence model (RNN, LSTM, GRU and Transformers) and explain the concepts in detail (Total Runtime: 5hr 55 mins)
- This video is by Prof. Chris Manning from the Stanford NLP course. In the following video titled “Recurrent Neural Networks”, Prof. Manning introduces Neural Dependency Parsing and Language models, which serves as a great build up for the introduction of Sequence Models (Runtime: 1 hr 19 mins)
- In this video titled “Simple and LSTM RNNs” from Stanford NLP course, Prof. Manning, goes into the topics of RNN, LSTM in detail (Runtime: 1 hr 21 mins)

