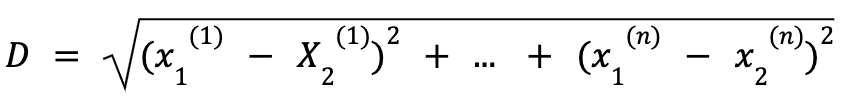The Euclidean Distance, or L2 norm, is the most common distance metric used in clustering. It measures the straight-line, or shortest, distance between observations in p-dimensional space. In two dimensions, the formula reduces to the commonly used Pythagorean theorem. For two observations x1 and x2, the Euclidean Distance is computed by the following, where the superscript denotes the dimension from 1 to n: